The Arduino Uno R3 is a microcontroller board based on a removable, dual-inline-package (DIP) ATmega328 AVR microcontroller. It has 20 digital input/output pins (of which 6 can be used as PWM outputs and 6 can be used as analog inputs). Programs can be loaded on to it from the easy-to-use Arduino computer program. The Arduino has an extensive support community, which makes it a very easy way to get started working with embedded electronics. The R3 is the third, and latest, revision of the Arduino Uno.
Overview
The Arduino Uno is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328. It has 20 digital input/output pins (of which 6 can be used as PWM outputs and 6 can be used as analog inputs), a 16 MHz resonator, a USB connection, a power jack, an in-circuit system programming (ICSP) header, and a reset button. It contains everything needed to support the microcontroller; simply connect it to a computer with a USB cable or power it with a
AC-to-DC adapter or battery to get started.
The Uno differs from all preceding boards in that it does not use the FTDI USB-to-serial driver chip. Instead, it features the Atmega16U2 programmed as a USB-to-serial converter. This auxiliary microcontroller has its own USB bootloader, which allows advanced users to reprogram it.
The Arduino has a large support community and an extensive set of support libraries and hardware add-on "shields" (e.g. you can easily make your Arduino wireless with our
Wixel shield), making it a great introductory platform for embedded electronics. Note that we also offer an
Arduino starter kit and the
Arduino Inventor's Kit, both of which include an Arduino Uno along with an assortment of components (e.g. breadboard, sensors, jumper wires, and LEDs) that make it possible to create a number of fun introductory projects.
This is the 3rd revision of the Uno (R3), which has a number of changes:
- The USB controller chip changed from ATmega8U2 (8K flash) to ATmega16U2 (16K flash). This does not increase the flash or RAM available to sketches.
- Three new pins were added, all of which are duplicates of previous pins. The I2C pins (A4, A5) have been also been brought out on the side of the board near AREF. There is a IOREF pin next to the reset pin, which is a duplicate of the 5V pin.
- The reset button is now next to the USB connector, making it more accessible when a shield is used.
More information about the
Arduino Uno R3 is available on Arduino's website.
Summary
- Microcontroller: ATmega328
- Operating voltage: 5 V
- Input voltage (recommended): 7-12 V
- Digital I/O pins: 20 (of which 6 provide PWM output)
- Analog input pins: 6*
- DC current per I/O pin: 40 mA
- DC current for 3.3V pin: 50 mA
- Flash memory: 32 KB (ATmega328) of which 0.5 KB used by bootloader
- SRAM: 2 KB (ATmega328)
- EEPROM: 1 KB (ATmega328)
- Clock speed: 16 MHz
*The Arduino Uno has 20 total available I/O lines; all of them can function as digital I/O lines, and six of them can be used as analog inputs.
Choosing the Right Controller
The table to the right compares the Arduino Uno to
Orangutan robot controllers, which are based on the same AVR architecture and feature integrated motor drivers and additional hardware suitable for robotics applications. We also offer the Basic Stamp, which offers a lot of support and educational materials for beginners, and the much higher performance
mbed development board, which is based on a 96 MHz 32-bit ARM Cortex M3. See their product pages for more information.
Dimensions
| Size: |
2.95" x2.1" |
| Weight: |
28 g |
General specifications
| Processor: |
ATmega328 @ 16 MHz |
| RAM size: |
2048 bytes |
| Program memory size: |
31.5 Kbytes |
| Motor channels: |
0 |
| User I/O lines: |
20
1 |
| Max current on a single I/O: |
40 mA |
| Minimum operating voltage: |
7 V |
| Maximum operating voltage: |
12 V |
| Reverse voltage protection?: |
N |
| External programmer required?: |
N
2 |
Notes:
- 1
- All 20 can be used as digital I/O and 6 can be used as analog inputs.
- 2
- An external programmer is required for setting the fuses or upgrading the bootloader.
-
Recommended links
- Arduino Uno R3
- Detailed description of the Arduino Uno R3.
- How to get Arduino running on Windows
- A tutorial for setting up an Arduino environment on Windows.
- Arduino Software
- Arduino integrated development environment (IDE) software
- Arduino Programming Reference
- Arduino Forum
- LSM303 Arduino library
- This is a library for the Arduino that interfaces with our LSM303DLM and
LSM303DLHC 3D compass and accelerometer carriers as well as the compass and accelerometer ICs on the MinIMU-9 and MinIMU-9 v2 (it also works with the LSM303DLH on older versions of those boards). It makes it simple to configure the device and read the raw accelerometer and magnetometer data, and it has a function for computing the tilt-compensated heading for those looking to use the LSM303 as a tilt-compensated compass.
-
- L3G4200D and L3GD20 Arduino library
- This is a library for the Arduino that interfaces with our L3G4200D and
L3GD20 3-axis gyro carriers as well as the gyros on theMinIMU-9 and
MinIMU-9 v2. It makes it simple to configure the device and read the raw gyro data.
-
- MinIMU-9 + Arduino AHRS
- This Arduino program (sketch) allows an
Arduino connected to a
MinIMU-9 or
MinIMU-9 v2 to function as an attitude and heading reference system, calculating estimated roll, pitch, and yaw angles from sensor readings that can be visualized with a 3D test program on a PC. It is based on the work of Jordi Munoz, William Premerlani, Jose Julio, and Doug Weibel.
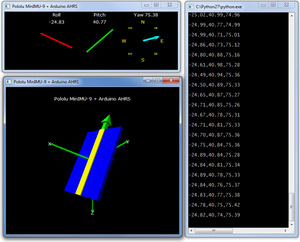 |
Visualization of AHRS orientation calculated from MinIMU-9 readings.
|
- Arduino Library for the Pololu QTR Reflectance Sensors
- This guide explains how to use the QTR Sensors library to read Pololu
QTR reflectance sensors and
QTR sensor arrays with
Arduinos and Arduino-compatible devices like the Pololu Orangutan robot controllers.
-
- Beacon Locating Robot â€" Powered by Arduino and IR Transceiver
- A beacon-chasing robot built with our IR Beacon, an RP5 Tracked Chassis, and an
Arduino. By Christopher Hazlett, December 2009.
-
- "How to use the TB6612FNG motor driver with the Arduino for noobs"
- This MeanPC.com guide explains how to control the
TB6612FNG Dual Motor Driver Carrier with an
Arduino.
-
-
-
No recommended products at the moment.
No recommended products at the moment.