The Baby Orangutan B-328 is a very compact but complete robot controller, packing a high-performance AVR microcontroller and two motor drive channels in the same 24-pin form factor as competing units that include just a microcontroller. You can connect your battery, sensors, and motors directly to this small module to make a miniature robot, or you can use the Baby Orangutan as an auxiliary controller in larger robots. This version includes Atmel's new ATmega328P microcontroller with 32 KB of program memory and 2 KB of RAM.
Overview
The Baby Orangutan is a complete control solution for small robots, all packed into a tiny 1.2" x 0.7" 24-pin DIP package. Its compact design eliminates bulkier components such as the LCD and switches while retaining the most essential features of the Orangutan robot controller line: a programmable ATmega48 or ATmega328P AVR microcontroller and a dual H-bridge for direct control of two DC motors. This integrated motor driver sets the Baby Orangutan B apart from similarly-sized microcontroller boards from other manufacturers. Two on-board indicator LEDs, a trimmer potentiometer, a 20 MHz resonator, and reverse battery protection round out the basic hardware features of the Baby Orangutan.
The removal of the larger Orangutan components also allows for a significantly improved manufacturing process that allows Pololu to offer the Baby Orangutan B at a very affordable price. Because the Orangutans are based on Atmel's powerful AVR microcontrollers, the Orangutans deliver significantly higher performance than other similar controller boards. The availability of free development software, such as Atmel's
AVR Studio IDE and the
WinAVR GCC C/C++ compiler, and low-cost programmers, such as the Pololu USB AVR programmer, make the Baby Orangutan B a truly outstanding value. We offer a
combination deal that lets you save when you buy a USB AVR programmer with your Baby Orangutan.
For those not necessarily interested in robotics, the Baby Orangutan B is also a great introduction to the AVR microcontrollers because of its size and price. All you need to get started is a low-cost programmer and a power source. You can fit a substantial design even on a small breadboard since you won't need the space for basic components such as the voltage regulator and resonator. The source code for several sample projects is available under our resources tab; these examples are intended to help you get up and running quickly with your new AVR-based controller.
Specifications & On-Board Hardware
- overall unit dimensions: 1.2" x 0.7"
- input voltage: 5-13.5 V (15 V absolute maximum)
- two bidirectional motor ports can deliver ~1 A continuous (3 A peak) per channel
- programmable 20 MHz Atmel ATmega48 AVR microcontroller (4 KB flash, 512 bytes SRAM, 256 bytes EEPROM) or Atmel ATmega328P AVR microcontroller (32 KB flash, 2 KB RAM, 1 KB EEPROM)
- 18 user I/O lines, 16 of which can be used for digital I/O and 8 of which can be used as analog input channels
- 1 user LED
- user potentiometer tied to ADC7
- 20 MHz external resonator
- pinout is compatible with the Orangutan SV-328 and Orangutan LV-168, so the same code will generally work on all of these devices
ATmega48, ATmega168, and ATmega328 comparison
The Baby Orangutan B is available with either the
ATmega48 or
ATmega328P AVR microcontroller (the ATmega168 version has been discontinued). The main differences between the mega48 and mega328P are memory size, boot loader support, and interrupt vector size. The mega328 can also run at lower voltages than the mega48 and mega168 for frequencies below 10 MHz.
|
mega48 |
mega168 |
mega328P |
| Flash |
4K Bytes |
16K Bytes |
32K Bytes |
| RAM |
512 Bytes |
1024 Bytes |
2048 Bytes |
| EEPROM |
256 Bytes |
512 Bytes |
1024 Bytes |
| Interrupt Vector Size |
1 instruction word/vector |
2 instruction words/vector |
2 instruction words/vector |
| Boot Loader Section |
none |
128, 256, 512, or 1024words
(256, 512, 1024, or 2048 bytes) |
256, 512, 1024, or 2048words
(512, 1024, 2048, or 4096 bytes) |
Note: As of July 25, 2011, the
Baby Orangutan B-48 is only available for high-volume orders. Please contact us if you are interested in placing such an order. The Baby Orangutan B-328 continues to be available as normal.
Included components
The compact module can be used as a DIP component on breadboards or prototyping boards, or the pin-less versions can be used for space-constrained installations in miniature robots. The 0.1" header pins are included with the Baby Orangutan B but are not soldered in. Power pins, one of the motor outputs, and several I/O lines are all accessible from one side to enable use of the Baby Orangutan as a single in-line pin (SIP) package for applications that do not require all of the I/O lines. The small size and low cost of the Baby Orangutan makes it a perfect option for primary control of small robots or for auxiliary control on larger robots.
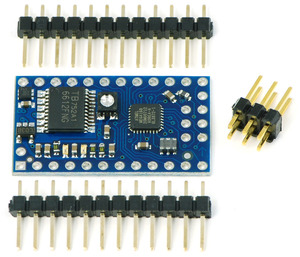 |
| Baby Orangutan B with included 0.1" header pins. |
|
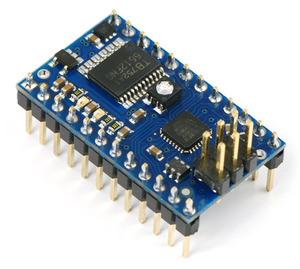 |
| Baby Orangutan B with included header pins soldered in for breadboard installation. |
|
Note: The Baby Orangutan B-168 has been replaced by the
Baby Orangutan B-328, which uses the newer ATmega328P microcontroller to provide 32 KB of program memory, 2 KB of RAM, and 1 KB of EEPROM. The ATmega328P is essentially a drop-in replacement for the ATmega168, so the code that works on the Baby Orangutan B-168 should work with minimal modification on the Baby Orangutan B-328 (the
Pololu AVR Library now supports the ATmega328P).
========================================
Dimensions
| Size: |
1.20" x 0.70" |
| Weight: |
1.5 g
1 |
General specifications
| Processor: |
ATmega328P @ 20 MHz |
| RAM size: |
2048 bytes |
| Program memory size: |
32 Kbytes |
| Motor driver: |
TB6612FNG |
| Motor channels: |
2 |
| User I/O lines: |
18
2 |
| Max current on a single I/O: |
40 mA |
| Minimum operating voltage: |
5 V |
| Maximum operating voltage: |
13.5 V |
| Continuous output current per channel: |
1 A |
| Peak output current per channel: |
3 A |
| Maximum PWM frequency: |
80 kHz |
| Reverse voltage protection?: |
Y |
| External programmer required?: |
Y |
| LCD included?: |
N |
Notes:
- 1
- without headers
- 2
- 16 can be used as digital I/Os and 8 can be used as analog inputs.
========================================
Documentation and other information
 Pololu Baby Orangutan B User's Guide(Printable PDF:
baby_orangutan_b.pdf)
Pololu Baby Orangutan B User's Guide(Printable PDF:
baby_orangutan_b.pdf)
User's guide for the Pololu Baby Orangutan B-48, B-168, and B-328 robot controllers.
 Pololu AVR C/C++ Library User's Guide(Printable PDF:
pololu_avr_library.pdf)
Pololu AVR C/C++ Library User's Guide(Printable PDF:
pololu_avr_library.pdf)
Information about installing and using the C/C++ libraries provided for use with Pololu products.
 Pololu AVR Library Command Reference(Printable PDF:
avr_library_commands.pdf)
Pololu AVR Library Command Reference(Printable PDF:
avr_library_commands.pdf)
A reference to commands provided in the Pololu C/C++ and Arduino libraries for the AVR.
 Programming Orangutans and the 3pi Robot from the Arduino Environment(Printable PDF:
orangutan_arduino.pdf)
Programming Orangutans and the 3pi Robot from the Arduino Environment(Printable PDF:
orangutan_arduino.pdf)
Guide to making the Arduino IDE compatible with the 3pi robot and the Orangutan SV-168, Orangutan LV-168, and Baby Orangutan B robot controllers, including Arduino libraries for interfacing with the all of their on-board hardware.
 Application Note: Using the Motor Driver on the 3pi Robot and Orangutan Robot Controllers(Printable PDF:
motor_driver_application_note.pdf)
Application Note: Using the Motor Driver on the 3pi Robot and Orangutan Robot Controllers(Printable PDF:
motor_driver_application_note.pdf)
Detailed information about the 3pi Robot, Orangutan SV-328/168 and LV-168, and Baby Orangutan B motor drivers, including truth tables and sample code.
 Application Note: MLX90614ESF SMBus Communication with Orangutan Robot Controllers(Printable PDF:
mlx90614esf_smbus_orangutan.pdf)
Application Note: MLX90614ESF SMBus Communication with Orangutan Robot Controllers(Printable PDF:
mlx90614esf_smbus_orangutan.pdf)
A guide for implementing the SMBus (I2C-compatible) protocol for the MLX90614ESF temperature sensor on the AVR-based Orangutan robot controller series. The guide includes sample code for taking temperature readings.
File downloads
- Pololu AVR Development Bundle for Windows (release 110624) (173MB exe)
- This bundle contains the software you need to get started programming AVRs in Windows using the Pololu USB AVR Programmer: the WinAVR tools, Atmel AVR Studio 4, the Pololu AVR C/C++ Library, the Pololu USB AVR Programmer drivers and software, and the Pololu Orangutan SVP drivers.
- Toshiba TB6612FNG motor driver datasheet(308k pdf)
- Sample AVR Studio project for the ATmega48 to blink an LED(9k zip)
- This is a sample AVR Studio project that will blink an LED on an Baby Orangutan B-48.
- Sample AVR Studio project for the ATmega168 to blink an LED(9k zip)
- This is a sample AVR Studio project that will blink an LED on an Orangutan with an ATmega168 microcontroller: Orangutan mega168, Orangutan LV-168, Orangutan SV-168, Baby Orangutan mega168, and Baby Orangutan B-168.
- Sample AVR Studio project for the ATmega328P to blink an LED(9k zip)
- This is a sample AVR Studio project that will blink an LED on a Baby Orangutan B-328, 3pi robot, or Orangutan SV-328.
- AVR Studio demo project #1 for the Orangutan SV-168 and LV-168(14k zip)
- C code for the mega168: This project demonstrates the fundamentals of using I/O lines on a mega168. Each line of the source code is commented, and there is a short tutorial in comments at the start of main() on using AVR I/O and on C bit-logic. The program will alternately flash the two user LEDs until you ground the general-purpose I/O pin PD0 (the right-most of the eight user I/O lines at the top of the board). Grounding pin PD0 will cause the program to pulse the buzzer pin instead of the LED pins, causing the buzzer to play a note. While intended for use on the Orangutan SV-168 and LV-168, this program will run on the Baby Orangutan B-168 and can serve as a useful example on how to use the ATmega48/168 I/O lines. It will run on the Baby Orangutan B-328 with some minor modifications.
- LSM303DLH Orangutan example project(5k zip)
- This sample program shows how to use an
LSM303DLH 3D compass and accelerometer carrier with an Orangutan robot controller to build a tilt-compensated digital compass. The AVR Studio project is set up for an ATmega328P microcontroller, but it will work on other Orangutans with simple changes to the project configuration.
Recommended links
- WinAVR
- A free, open-source suite of development tools for the AVR family of microcontrollers, including the GNU GCC compiler for C/C++.
- AVR Studio
- Atmel's free AVR integrated development environment (IDE) that works with WinAVR's free GCC C/C++ compiler.
- ATmega328P documentation
- Atmel's product page for the ATmega328P.
- ATmega168 documentation
- Atmel's product page for the ATmega168.
- ATmega48 documentation
- Atmel's product page for the ATmega48.
- Pololu Orangutan Forum Section
- The Orangutan discussion section of the Pololu Robotics Forum.
- AVR Freaks
- AVR community with forums, projects, and AVR news.
- Orangutan-lib
- An open-source C library for the Orangutan family of robot controllers. Note:this library was not created by and is not maintained by Pololu; it contains only limited support for the Orangutan X2 and does not directly support the Orangutan SV-168, Orangutan LV-168, or Baby Orangutan B revision.
- Tutorial: AVR Programming on the Mac
- Customer Michael Shimniok has written a guide to programming AVRs (the Orangutan LV-168, specifically) using the Mac.
- Robot Zero: a fast line follower for beginners
- A guide to building a fast (> 2 m/s) line-following robot from scratch. By C.I.r.E., February 2011.
No recommended products at the moment.
No recommended products at the moment.